Electro-L1
|
Electro-L №1,
Russian _hydro-meteorological spacecraft, was launched on geostationary orbit on January 20, 2011
at 12:29 UTC by a Zenit rocket from Tyuratam (Baikonur Cosmodrome), Kazakhstan. Orbit parameters: perigee ~36,000 km, apogee ~36,000 km,
latitude 0°, longitude 76°. It is also known as GOMS 2, or Geostationary Operational Meteorological Satellite 2.
Electro-L №1 will capture real-time images of clouds and storm systems, collecting weather imagery several
times per hour with visible and infrared cameras. The satellite's position in geosynchronous orbit will yield
views of the entire Earth disk, allowing its weather sensors to observe storm systems across a wide swath of Asia,
the Middle East, and the Indian Ocean. The satellite will also study space weather phenomena and provide communications
for search-and-rescue services. The satellite weighs 1,701 kg and will be parked at 76° E longitude.
It is expected to function for up to ten years.
The initial orbital parameters were period = 1,436.09 minutes, apogee = 35,793.8 km, perigee = 35,779.3 km,
inclination = 0.3° on 2011 Mar 30 at 20:01:56 UTC.
SKL-E spectrometer has been installed on-board to register energetic particles originated from Earth's radiation belts or from Solar flares. Spectrometer is directed southward, perpendicular to satellite orbit plane.
(more in
English
... Russian...)
SKL-E spectrometer parameters and energy ranges of registered particles
| Parameter |
energy ranges of
registered particles |
| electrons |
protons |
| P1 |
170-300 keV |
> 1.2 MeV |
| P2 |
> 2.3 MeV |
>13,5 MeV |
| P3 |
2.3 – 4.2 MeV |
- |
| P4 |
4.2 – 6.0 MeV |
- |
| P5 |
6 – 20 MeV |
- |
| P6 |
- |
13,5 – 23 MeV |
| P7 |
- |
23 – 42 MeV |
| P8 |
- |
42 – 112 MeV |
| P9 |
- |
112 – 320 MeV |
| P10 |
>1.3 MeV |
1.2 – 95 MeV |
| P11 |
- |
> 100 MeV |
|
|

|
SKL-E SPECTROMETER ON-BOARD ELECTRO-L SPACECRAFT
|
Electro-L, Russian hydro-meteorological spacecraft, was launched on geostationary orbit on January 20, 2011. Orbit parameters: perigee 36,000 km, apogee 36,000 km, latitude 0°, longitude 76°.
SKL-E ( spectrometer of cosmic rays for Electro) spectrometer has been installed on-board to register energetic particles originated from Earth's radiation belts or from Solar flares. Spectrometer is directed southward, perpendicular to satellite orbit plane
SKL-E spectrometer is a telescope. It consists of a communicating semiconductor and two scintillators, between which an absorber (~7 mm Al) is placed to ensure the demanding energy range (the primitive drawing of the spectrometer is presented in Fig.): -
D1 semiconductor of the dE/dx type has the 300 µcm Si thickness of the sensitive layer;
-
D2 scintillator on the base of CsJ(Tl) crystal has a h20xØ15 mm dimension;
-
D3 scintillator on the base of CsJ(Tl) crystal has a h5xØ15 mm dimension.
A collimator from brass selects the view cone of ~30°. Each detector is placed into a separate cover to make accessible to calibration. Covers were made from brass with the 11 mm thickness.
CsJ(Tl) crystals are coated with white enamel and orthalast tape. The bottom butt-end of crystals (without coating) has the optical contact with a photodiode.
The entrance window of the D1 detector is shielded by a 20 µcm Al foil. To displace of energy ranges for protons and electrons, registered by D2, a ~0.6 mm Al shielding is placed between D1 and D2 detectors. In this way, the total thickness of protection of the D2 entrance window came to ~1 mm Al.
Calculated energy ranges of registered particles are presented in a Table. The calculated geometric factor of the spectrometer is G=0.25 cm2·st.
The additional ~10 mm Al shielding is placed between D2 and D3 detectors: protons at the energy <100 MeV do not penetrated through D1 and D2 into D3. Protons at Ep>100 MeV can penetrate through the entrance window and the side-shielding and give insignificant contribution into P3, P4 and P5 results, that is to say to electron channels. This contribution can be taken into consideration during data processing with the help of P11 reading.
|
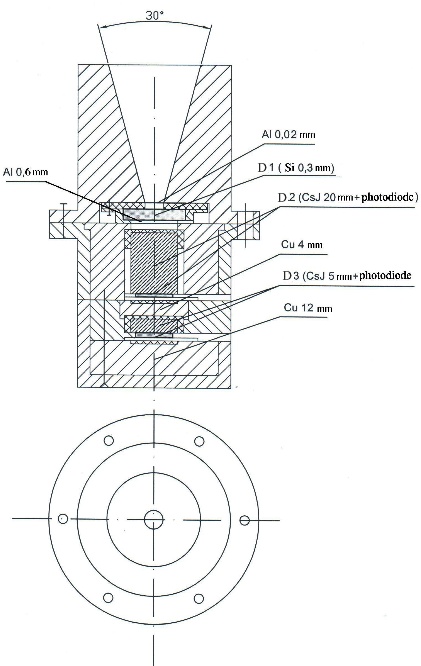
Fig. The primitive drawing of the SKL-E spectrometer
|
|
Спектрометр СКЛ-Э ИСЗ «ЭЛЕКТРО-Л»
ИСЗ «Электро-Л» — Российский космический аппарат гидрометеорологического назначения запущен 20 января 2011 года на геостационарную орбиту (перигей — 36,000 км; апогей — 36,000 км; долгота — 76°; широта — 0°).
Спектрометр СКЛ-Э предназначен для регистрации электронов радиационного пояса Земли и протонов радиационного пояса Земли и солнечных вспышек. Регистрация осуществляется в направлении перпендикулярном плоскости орбиты, на юг.
Спектрометр СКЛ-Э представляет собой телескоп из проходного полупроводникового детектора и двух сцинтилляционных детекторов, между которыми помещен поглотитель (7 мм Al) для обеспечения требуемого диапазона энергии (схематический чертеж приведен на рис.):
-
полупроводниковый детектор Д1 (типа dE/dх) с толщиной чувствительного слоя ~300 мкм Si;
-
сцинтилляционный детектор Д2 на основе кристалла CsI(Tl) размером h20хØ15 мм;
-
сцинтилляционный детектор Д3, выполненный также на основе кристалла CsI(Tl), но размером h5xØ20 мм.
Латунный коллиматор выделяет конус обзора ~30°. Каждый детектор расположен в отдельной упаковке, обеспечивающей удобство доступа для калибровки. Секции выполнены из латуни толщиной 11 мм.
Кристаллы CsI(Tl) покрыты белой эмалью и ортоластовой лентой. Нижний торец кристаллов (без покрытия) находится в оптическом контакте с фотодиодом.
Входное окно детектора Д1 экранировано фольгой ~20 мкм Al. Для смещения энергетического диапазона протонов и электронов, регистрируемых Д2, между детекторами Д1 и Д2 устанавливается экран ~0.6 мм Al, и, таким образом, общая толщина защиты входного окна Д2 составляет ~1 мм Al.
Значения энергий регистрируемых частиц приведены в таблице. Расчетный геометрический фактор спектрометра СКЛ-Э - G=0.25 см2·стер.
|
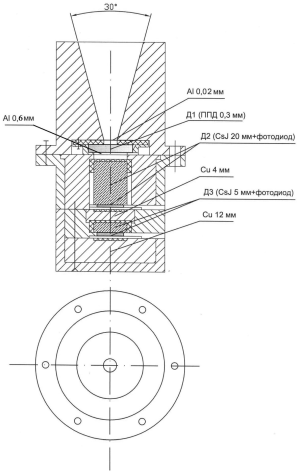
Схематический чертеж спектрометра СКЛ-Э
|
Charged particle count rates measurement
Data available from 2011-04-07 till 2016-10-04
SKL
Yearly data
|



